Here is a guide to forwarding requests to a server on local LAN from FreedomBox.
Goal
- You have a FreedomBox running with a working domain already setup. You are able to access your FreedomBox using a URL such as https://www.mysite.example/ .
- You have a different server running a local service on LAN that you wish to expose to the Internet on the same domain as your FredomBox. The local service must be a web service using the HTTP protocol (it is also possible to setup non-HTTP service, but that is a different approach). Optionally, you can have special domain assigned specifically for this local service.
- You wish for FreedomBox to handle the TLS certificates for this domain as FreedomBox typically does. Your local service need not setup and manage TLS certificates.
- Optionally, you may want to limit access to local service using FreedomBox credentials. Only users with a FreedomBox account (and belonging to a chosen group) will be able to access this service. The local service will not be available to general public on the Internet. This way you can host local services that don’t implement their own authentication or local services with their own authentication mechanisms disabled.
Exposing Local LAN servers to Internet using FreedomBox
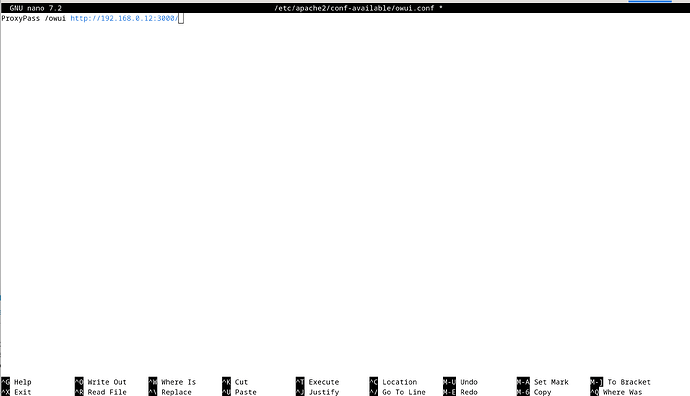
- To expose the service, create an Apache configuration file in
/etc/apache2/conf-available/ and write a ProxyPass directive. Assuming your local service is running on a computer with IP address 192.168.0.20 on port 3000, you can do this by running a command (as a root user on the terminal):
cat > /etc/apache2/conf-available/my-local-service.conf <<EOL
ProxyPass /myservice http://192.168.0.20:3000/
EOL
- Then, enable this Apache configuration. Run the following command:
a2enconf my-local-service
- Then reload Apache web server.
systemctl reload apache2
You can now access your local service at the following URL https://www.mysite.example/myservice/ . Note that the URL is a secure URL with https://. The certificates will be managed by FreedomBox/Let’s Encrypt. All your other apps and services work as usual. You can add any number services you want this way.
Running the Service on FreedomBox Itself
The above approach will also work if the local service is running on FreedomBox itself. In this case, the ProxyPass directive in the configuration should be modified to look like ProxyPass /myservice http://127.0.0.1:3000/.
Disabling the service
To disable exposing the local service:
- Disable the Apache configuration file.
a2disconf my-local-service
- Then, reload Apache web server.
systemctl reload apache2
Adding Authentication
You can configure the service to be available to only users with FreedomBox account. This is a good choice if:
- The local service that is exposed to the Internet should not be available to everyone. And,
- The local service does not provide its own authentication mechanism. Or,
- The local service provides it’s own authentication but you don’t want to maintain a different set of user accounts for that service and want to reuse your FreedomBox user accounts.
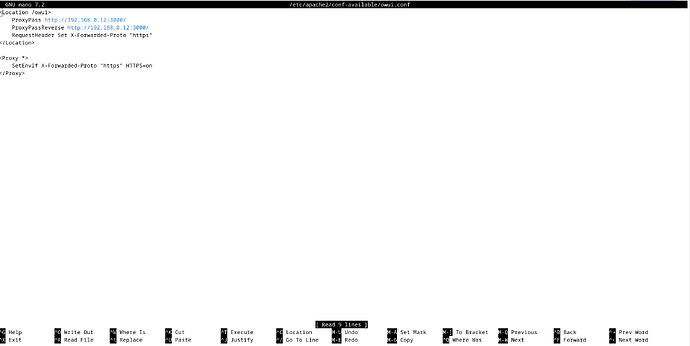
- Update the Apache configuration file
/etc/apache2/conf-available/my-local-service.conf to look like the following.
<Location /myservice/>
Include includes/freedombox-single-sign-on.conf
ProxyPass http://192.168.0.20:3000/
</Location>
- Then, reload Apache web server.
systemctl reload apache2
If you wish for only some groups of users to be able to access the service, another change to the configuration is needed. Make the configuration look like the following if you wish to allow users of “web-search” group and also users of “admin” group to access the local service. All other users even if they have a valid FreedomBox account will be denied access.
<Location /myservice/>
Include includes/freedombox-single-sign-on.conf
<IfModule mod_auth_pubtkt.c>
TKTAuthToken "web-search" "admin"
</IfModule>
ProxyPass http://192.168.0.20:3000/
</Location>
Hosting the Service on a Separate Domain
Some services and web applications hosted under a URL fragment such as /myservice/ do not work well. They require an entire domain or subdomain to be dedicated to them. In these cases too, FreedomBox can expose local services.
- First acquire a domain or a subdomain.
- If your domain is a custom domain that you own, go to the DNS settings on your domain name provider and add a subdomain. You can create a CNAME record that simply points to the main domain.
- If you are using FreedomBox Dynamic DNS service, then login into https://ddns.freedombox.org and enable the “Wildcard” option.
- Add the new domain into FreedomBox. Goto System → Name Services → Domain (regular) → Add. For example, add
myservice.mysite.example.
- Then create an Apache configuration file at
/etc/apache2/includes/<domainname>-include.conf. For our example this is: /etc/apache2/includes/myservice.mysite.example-include.conf. The contents of the file should be:
ProxyPass / http://192.168.0.20:3000/
- Modify the above file for authentication if necessary by adding the
Include and <IfModule> configuration directives as shown in the authentication section above.
Troubleshooting
When your setup does not work as expected, to debug, run a temporary web service on your FreedomBox.
- Create a temporary directory with an
index.html page on the FreedomBox.
mkdir temp
cd temp
cat > index.html <<EOL
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, World!</h1>
</body>
</html>
EOL
- Run a temporary web server (press Control-C to terminate):
python3 -m http.server 3000
- Update the Apache configuration to point to this temporary service on FreedomBox.
ProxyPass /myservice http://127.0.0.1:3000/
Extras
There are many additional features that Apache can provide to improve the local service. For these, explore Apache documentation. Some features include:
- Serving static files such as JS, CSS, and media files from local directory without invoking the local service to improve performance.
- Caching the responses from the local service to improve performance.
- Setting additional headers for security, cache control, etc.
- Modify the HTTP header responses from the service when it does not work well to hosting under a URL fragment such as
/myservice/.
- Perform redirects from
http:// URL to https:// and setting HSTS header.
- Load balancing among multiple local services for high availability, scaling, etc.
- And more.